|
|
 |
 |
|
Click on the Parashah name to read the summary:
|
 |
 |
|
The Intercession of Moses...
|
 |
 |
|
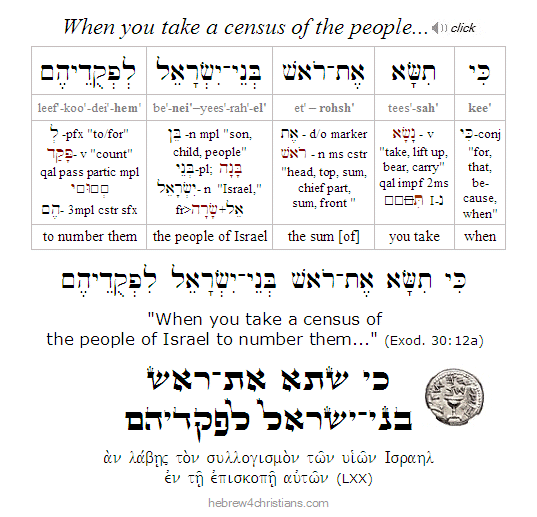
In our last two Torah readings (Terumah / Tetzaveh), Moses was upon Mount Sinai receiving the vision of the Sanctuary (i.e., the Mishkan or "Tabernacle") and its various furnishings. In this week's portion, God commanded that all Israelite men over the age of twenty were required to pay a tax for the upkeep of the Sanctuary: "each shall give (וְנָתְנוּ) a ransom (i.e., kofer: כּפֶר) for his life to the LORD" (Exod. 30:12). After this tax was defined, the LORD described some additional elements that would be required for the priestly service at the Sanctuary, namely, a copper washstand, sacred anointing oil, and incense for the Golden Altar in the Holy Place. The Lord then named Betzalel ben Uri (בְּצַלְאֵל בֶּן־אוּרִי), a man "filled with the Spirit of God" to be the chief architect of the Mishkan. Before the construction would begin, however, the Lord warned the people to be careful to observe the Sabbath day. Immediately following this admonition, God gave Moses the two tablets of the Ten Commandments, which were inscribed directly by the hand of God.
Before Moses returned to the camp, however, "certain people" had talked his brother Aaron into making a golden idol (עֵגֶל מַסֵּכָה) which they began to worship as their "god." The LORD then told Moses of their treachery and threatened to destroy all the Israelites, but Moses interceded on their behalf. As he rushed down the mountain, with the tablets in hand, he saw the people dancing about the idol and smashed the Tablets in anger. Moses then destroyed the idol and led the Levites in slaying 3,000 of the ringleaders.
The following day, Moses returned up the mountain and begged God to reaffirm the covenant. After a 40 day period of intercession, the Lord finally told Moses to carve a second set of Tablets and to meet him again at the summit of Sinai, where He would show Moses his glory and reveal to him the meaning of His Name (יהוה). When Moses encountered the LORD in a state of brokenness and forgiveness, his face began to shine with glory - a glory that foretold of the New Covenant of God's mercy and grace to come in Yeshua.
When the people saw Moses coming down the mountain with the second set of Tablets, they understood their sins were purged and that the Covenant had been renewed. When they approached him, however, they drew back in fear, because his face was radiant with the glory of God. Moses reassured them, however, and then told them all that the Lord had commanded while he was on the mountain. When Moses had finished speaking with them, he put a veil (מַסְוֶה) over his face. From that time on, Moses wore a veil in the camp, though he removed it whenever he went before the Lord for further instructions.
|
 |
 |
|
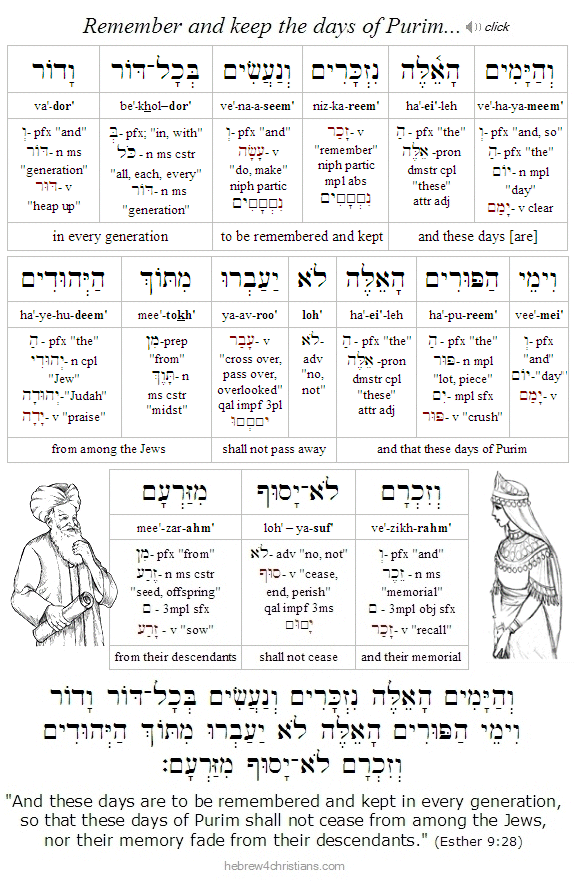
The holiday of Purim (פּוּרִים) celebrates the victory of the Jewish people over the dark forces of anti-Semitism in the world. In a sense, the entire holiday is a spoof or joke made at the expense of those who senselessly hate the Jewish people (and who therefore hate the God of Israel). Purim is therefore both a time of irony and a time to celebrate how God secretly acts on behalf of His people so that they will eventually triumph over their enemies.
Throughout the centuries and in various places, many have tried to destroy the Jewish people, but none has succeeded. עַם יִשְׂרָאֵל חַי / am Yisrael chai: "The people of Israel live!" Israel is God's "super sign" that He is faithful to His covenant promises (Jer. 31:35-37). Christians likewise can trust that God's sovereign hand works all things together for good -- even if at times things appear bleak and desperate (Rom. 8:28).

Megillat Esther, dating from the 1700's
This year Purim begins sundown, Monday March 2nd and continues until nightfall the next day. On the calendar, Monday at sundown marks the 14th of the month of Adar, the day after Haman's roll of the dice indicated that the 13th of Adar was most "propitious" date to exterminate the Jews of Persia. Note that Purim is celebrated the day after since it was at that time that the Jews experienced the joy of their deliverance (in Israel, Purim is observed a day later still (i.e., on Adar 15th) and is called Shushan Purim).
Hebrew Lesson:
Esther 9:28 reading (click for audio):
HAPPY PURIM CHAVERIM!
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Shabbat Parah - שבת פרה
|
|
|
|
Four "special Sabbaths" occur just before the start of spring: two before Purim and two before Passover. Collectively, these Sabbaths are called "The Four Shabbatot" and one of four additional Torah readings (called Arba parashiyot) are read on each of these Sabbaths in preparation for the spring holidays. The names of these Sabbaths are Shabbat Shekalim, Shabbat Zakhor, Shabbat Parah, and Shabbat HaChodesh, respectively.
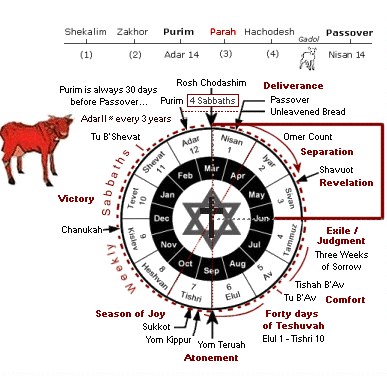 |
The Shabbat that immediately follows Purim is called Shabbat Parah - the "Sabbath of the Cow," when the chapter of the parah adumah (פָרָה אֲדֻמָּה), or the "Red Heifer" (Num. 19:1-22), is recited following the regular Torah service. The early sages chose this additional portion of Scripture to be reviewed at this time to help prepare for the coming New Year (i.e., Rosh Chodashim) and because the people were required to purify themselves before coming to Jerusalem for the pilgrimage festival of Passover.
The Red Heifer offering is considered a paradox to most Jewish thinkers, though it is clearly a picture of the Messiah Yeshua. The paradox is that the one who offers this sacrifice becomes ritually impure, while the sprinkling of the ashes is used to make people clean... The ritual is considered "chok" (חק) within the Jewish tradition, meaning that it makes no rational sense. In fact, the Talmud states that of all the taryag mitzvot (613 commandments), this is the only one that King Solomon could not fathom, since this sacrifice was regarded as the most paradoxical of all the sacrifices found in the Torah.
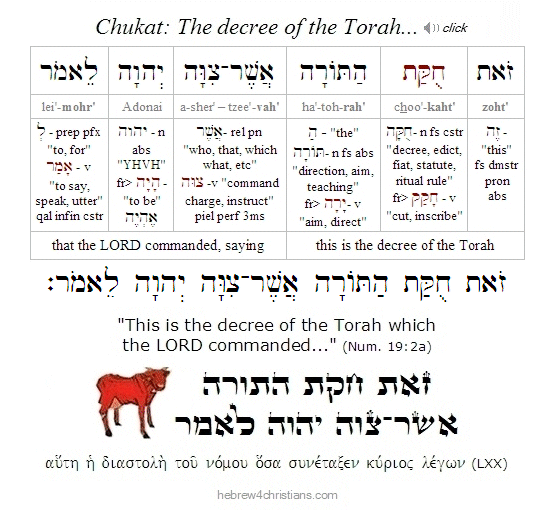 |
The Uniqueness of the Sacrifice
The Parah Adumah sacrifice was entirely unique, for the following reasons:
- It was the only sacrifice that specifically required an animal of a particular color. This animal was extremely rare and unique of its kind (in fact, Maimonides wrote, "Nine Parot Adumot were prepared from the time the Commandment was given until the destruction of the Second Temple. Moses our Teacher prepared one, Ezra prepared one and seven more were prepared until the Destruction of the Temple. The tenth will prepared by the Mashiach." (We would say "was prepared" by the Mashiach Yeshua, blessed be He.)
- It was the only sacrifice where all the rituals were carried out outside of the camp (and later, outside the Temple precincts). That is, the "blood applications" of this sacrifice occurred in a location apart from the altar (the Talmud recounts that the High Priest performed the blood applications of the Red Heifer while gazing at the Temple and at the Holy of Holies from a mountain opposite the Temple mount).
- It was the only sacrifice where the ashes were preserved and used (other sacrifices required the ashes be disposed outside of the camp).
- Hyssop, scarlet yarn, and a cedar stick would then be thrown upon the burning parah adumah (these same items were used to cleanse from tzara'at, skin disease). In other words, the blood was assimilated into the ashes of the sacrifice, which were then gathered and mixed with water to create the "water of separation" (mei niddah) for the Israelite community. Note that the word "separation" (niddah) refers to menstrual impurity and harkens to Zech. 13:1: "On that day there shall be a fountain opened for the house of David and the inhabitants of Jerusalem, to cleanse them from sin and from niddah."
- It was the only sacrifice that ritually contaminated the priest who offered it, but made the one who was sprinkled by it clean.
According to Jewish tradition, this sacrifice was to atone for the sin of the Golden Calf, though the Torah itself does not make this association. The LORD Yeshua, our Messiah, is the perfect fulfillment of the Parah Adumah, since He was completely without sin or defect (2 Cor 5:21; John 8:46); He was sacrificed outside the camp (Heb 13:13); He made Himself sin for us (2 Cor 5:21); His sprinkling makes us clean (1 Pet 1:2; Heb 12:24; Rev 1:5); and the "water of separation" that His sacrifice created is the means by which we are made clean from the impurity of sin (Eph 5:25-6; Heb 10:22).
For more about Shabbat Parah, click here.
The Haftarah for Shabbat Parah
The Haftarah read for Shabbat Parah (Ezek. 36:16-38) is ostensibly linked to the sacrifice of the Red Heifer, though on a deeper level it relates to Israel's national salvation and return to the promised land after the Great Tribulation period.... Despite the horrors of the worldwide Diaspora of the Jewish people and their faithlessness before the nations, God will be true to His promises by causing the Jews to finally accept His salvation (i.e., Yeshua) and to return to the land of Israel. At that time, "all Israel will be saved," as the Apostle Paul also foretold (Rom. 11:26). For more about this, see the Shabbat Parah page here.
|
|
|
|
Blessing before Torah Study:
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Some terms:
|
|
|
|
- Parashah is the weekly Scripture portion taken from the Torah. Each parashah is given a name and is usually referred to as "parashat - name" (e.g., parashat Noach). For more information about weekly readings, click here.
- Aliyot refer to a smaller sections of the weekly parashah that are assigned to people of the congregation for public reading during the Torah Reading service. In most congregations it is customary for the person "called up" to recite a blessing for the Torah before and after the assigned section is recited by the cantor. For Shabbat services, there are seven aliyot (and a concluding portion called a maftir). The person who is called to make aliyah is referred to as an oleh (olah, if female).
- Maftir refers to the last Torah aliyah of the Torah chanting service (normally a brief repetition of the 7th aliyah, though on holidays the Maftir portion usually focuses on the Holiday as described in the Torah). The person who recites the Maftir blessing also recites the blessing over the Haftarah portion.
- Haftarah refers to an additional portion from the Nevi'im (Prophets) read after the weekly Torah portion. The person who made the maftir blessing also recites the blessing for the Haftarah, and may even read the Haftarah before the congregation.
- Brit Chadashah refers to New Testament readings which are added to the traditional Torah Reading cycle. Often blessings over the Brit Chadashah are recited before and after the readings.
- Mei Ketuvim refers to a portion read from the Ketuvim, or writings in the Tanakh. Readings from the Ketuvim are usually reserved for Jewish holidays at the synagogue.
- Perek Yomi Tehillim refers to the daily portion of psalms (mizmorim) recited so that the entire book of Psalms (Tehillim) is read through in a month. For a schedule, of daily Psalm readings, click here.
- Gelilah refers to the tying up and covering the Sefer Torah (Torah Scroll) as an honor in the synagogue.
- Divrei Torah ("words of Torah") refers to a commentary, a sermon, or devotional on the Torah portion of the week.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Related Topics:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
<< Return
|
|
|
|
Hebrew for Christians
Copyright © John J. Parsons
All rights reserved.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|