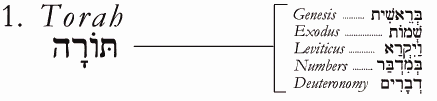|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Download a printable document listing the books of the Bible in Hebrew: |
|
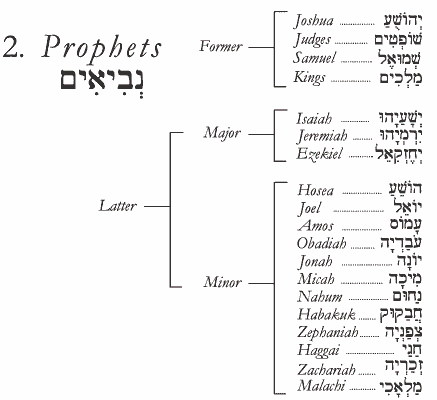
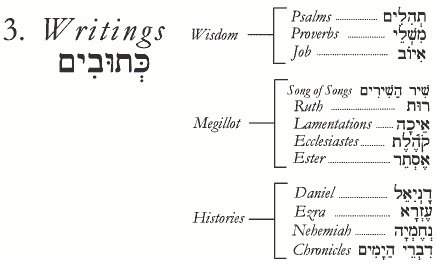
Three Divisions of Tanakh |
|||
|
|
Notes: |
|
|
The Thirteen Principles of Faith |
||||
|
Moses Maimonides (1135-1204) is considered by many Jews to be the most important medieval sage. Influenced by Thomas Aquinas and Avicenna, Maimonides sought to systematize the Jewish faith along scholastic lines. His Shloshah-Asar Ikkarim, or Thirteen Principles of the faith, is still widely recited as a sort of Jewish credo among many orthodox Jews. |
||||
|
Related Items: |
||||
|
|
|
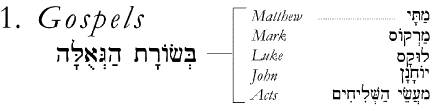
The B'rit Chadashah |
|
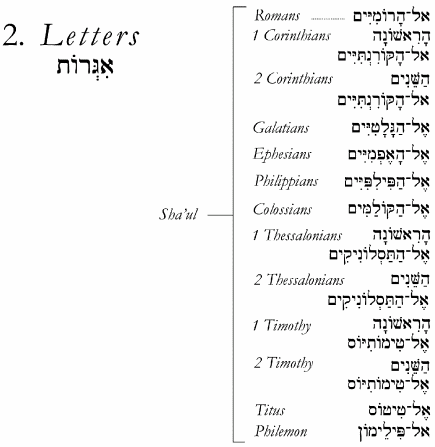
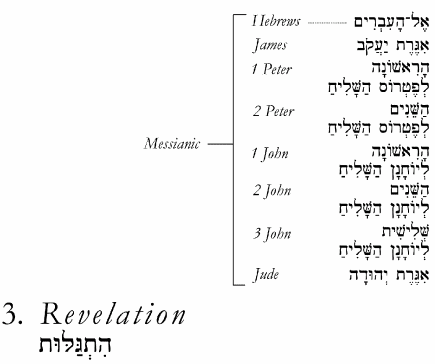
The New Testament is called the B'rit Chadashah in Hebrew (ūæų╝ų░ū©ų┤ūÖū¬ ūŚų▓ūōųĖū®ūüųĖūö), meaning "New Covenant" (the word B'rit means "covenant" and Chadashah means "new"). Like the Tanakh, it can be divided into three main parts: Gospels/Acts (corresponding to Torah), Letters (corresponding to Ketuvim), and Revelation (corresponding to Nevi'im): |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Download a printable Word document listing the books of the Bible in Hebrew: |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Like the Tanakh, the B'rit Chadashah can be divided into three main parts: Gospels/Acts (corresponding to Torah), Letters (corresponding to Ketuvim), and Revelation (corresponding to Nevi'im): |
|
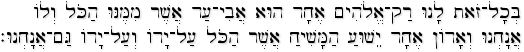 |
||||||||||
|
b'khol-zot lanu rak-elohim echad, hu avi-'ad, asher mimenu hakol v'lo anachnu, |
||||||||||
|
Yet for us there is one God, the Father, from whom are all things and for whom we exist, |
||||||||||
|
Notes: |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||